A broad overview from SEO specialist’s perspective.
Content
- Introduction
- Chapter 1: Polish economy, demographics and digital landscape
- Poland’s economic stability: a catalyst for e-commerce and investment
- Macroeconomic stability: a magnet for investors
- A strong economy fuels e-commerce growth
- Polish e-export: a growing frontier
- Implications for e-commerce and SEO in Poland
- Language and cultural factors
- Polish demographics in the context of e-commerce and SEO
- E-commerce dynamics in Poland: An in-depth Look
- Polish e-commerce in 2023 – brief summary
- Regulations and controlled niches
- Legal aspects of e-commerce in Poland
- Chapter 2: practical aspects of SEO in Poland
- SEO services in Poland
Introduction
Welcome to my guide on SEO (mostly for e-commerce) in Poland. I’m deeply rooted in the local market – since 2012 I run takaoto.pro, an agency that delivers SEO services primarily for e-commerce and enterprise clients mostly in Poland and other CEE markets. This article is crafted to share insights and strategies specific to SEO in Poland, aimed at both local and international professionals among SEO’s, marketers, e-commerce specialists, entrepreneurs and investors. I’ll guide you through effective ways to navigate the Polish SEO landscape.
Whether you’re fine-tuning your local SEO efforts or looking to make your mark in Poland in near future, this article is designed to support your success. If you need any support, contact me and I’ll be glad to guide you with professional SEO services and consulting. I can also match you with hi-end partners offering digital marketing services in different channels like SoMM, PPC, e-PR, Google Ads, SMS and e-mail.

Chapter 1: Polish economy, demographics and digital landscape
Poland’s economy is one of the largest in Central Europe, characterized by its robust growth and resilience in the face of global economic challenges. As a member of the European Union since 2004, Poland has experienced significant economic transformation, driven by investments in infrastructure, a skilled workforce, and an increasing focus on innovation and technology.
The country’s GDP has been on a consistent upward trajectory, making it an attractive destination for foreign investments.
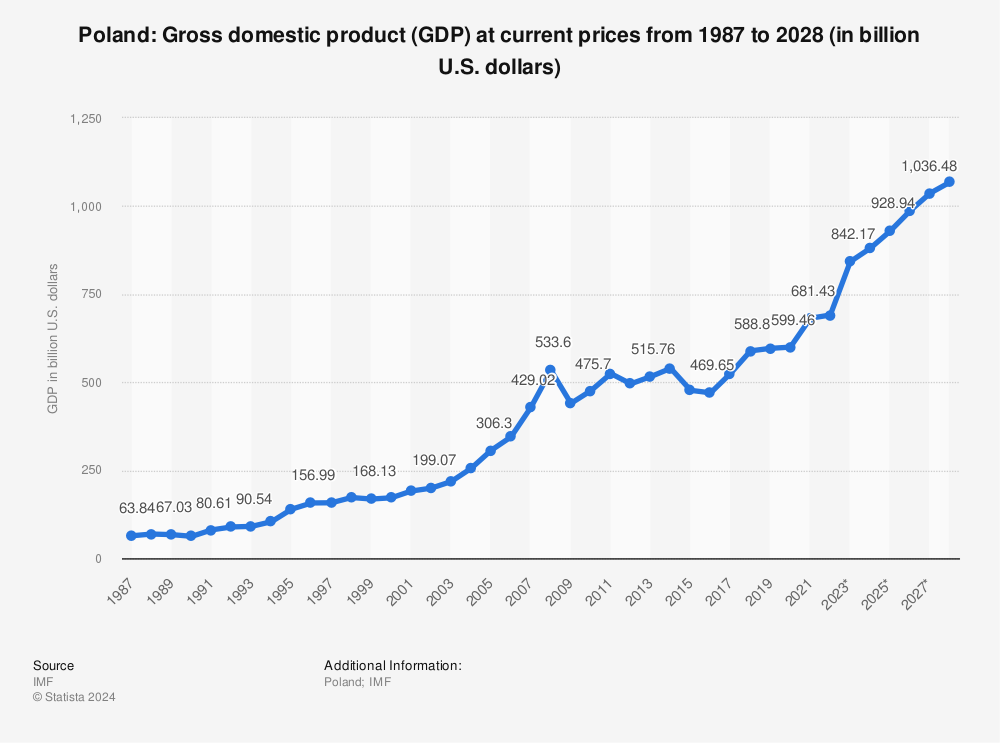
Poland’s economy is diverse, with significant contributions from sectors such as manufacturing, services, and information technology. The IT sector, in particular, has seen rapid growth, supported by a strong educational system that produces highly skilled professionals in engineering, IT, and related fields. This talent pool is a critical asset for the digital economy and has contributed to Poland’s reputation as a hub for IT services and software development in Europe.
E-commerce is another area of significant growth within the Polish economy. The convenience of online transactions, coupled with the increasing trust in digital payment systems, has propelled the e-commerce market to new heights. This growth is further facilitated by the country’s strategic location in Europe, offering excellent logistics and distribution networks that serve both domestic and international markets.
Poland’s digital landscape is a dynamic and rapidly evolving environment, reflecting the country’s growing economy and its increasing integration into the global digital economy.
With a population of over 38 million people, Poland boasts a high internet penetration rate, with over 93% of the households having access to the web. This widespread connectivity has fostered a vibrant online community and a competitive marketplace for both local and international businesses.
The Polish digital market is characterized by its openness to new technologies and platforms, with a significant portion of the population actively using social media, e-commerce sites, and various online services.
The country’s e-commerce sector, in particular, has seen substantial growth in recent years, driven by the convenience of online shopping and the expanding range of products and services available. This growth is supported by a well-developed logistics and delivery infrastructure, making online shopping a seamless experience for Polish consumers.
Search engines play a crucial role in the Polish digital landscape, with Google.pl dominating the market. However, local preferences and behaviors also influence search trends and online consumption patterns, making it essential for SEO professionals to understand the nuances of the Polish market. Additionally, the use of mobile devices to access the internet is on the rise, emphasizing the importance of mobile optimization in SEO strategies.
Source: gs.statcounter.com/search-engine-market-share/all/poland StatCounter Global Stats – Search Engine Market Share in Poland
The e-commerce sector in Poland, experiencing robust growth, is projected to reach significant value, reflecting a dynamic and expanding online marketplace. Google’s commanding presence, capturing over 95% of the search engine market share in Poland, underscores the critical importance of tailored SEO strategies. For SEO professionals, navigating this landscape requires a nuanced understanding of local consumer behaviors and preferences. By leveraging detailed insights into Poland’s digital ecosystem, businesses can develop SEO strategies that not only align with the preferences of Polish audiences but also capitalize on the burgeoning opportunities within this lively market.
Now let’s dive into details of how economic factors influence e-commerce and investments in Poland.
Poland’s economic stability: a catalyst for e-commerce and investment
Poland stands as a beacon of economic stability and robust growth in Central and Eastern Europe, and indeed across the continent. As the 6th largest economy in the European Union, with a GDP per capita exceeding 70% of the EU average, Poland’s consistent development over the past quarter-century is noteworthy. Remarkably, it was the only European nation to dodge the 2008-2010 recession, underscoring its solid economic foundation. The engines driving its growth? A healthy mix of exports and vigorous domestic consumption.
Macroeconomic stability: a magnet for investors
Poland’s allure for investors is not just its size or growth but its macroeconomic stability and the predictability it offers for long-term investment planning. The country’s public finances, boasting a debt-to-GDP ratio that’s the envy of many in the EU, coupled with its resilience during financial crises, make it an attractive destination for foreign investment. But what does this stability mean for the e-commerce sector and SEO strategies?
A strong economy fuels e-commerce growth
With the Polish economy growing at a pace well above the EU and Eurozone averages, consumer confidence is high. The rapid recovery post-2020, boasting a projected GDP growth of 4.6% in 2022, spells good news for e-commerce. A buoyant economy means more disposable income and, consequently, more spending online. This economic backdrop presents fertile ground for e-commerce players to thrive, underscored by the exponential growth of Poland’s online shopping sector.
Polish e-export: a growing frontier
While Polish e-commerce is on a remarkable upswing, it’s interesting to note that e-export—selling goods and services abroad through websites or mobile apps—constitutes less than 20% of Polish companies’ online sales. According to data from the Central Statistical Office (GUS) in 2016, Polish firms engaged in e-commerce exported goods and services worth over 27.5 billion PLN, which represented 16% of their total online sales revenue.
It’s crucial to highlight that these figures do not account for the activities of micro-enterprises (employing up to 9 people), whose contribution to e-export could be significantly more substantial than in traditional export sectors. This suggests their potential impact on the total value of foreign electronic sales might be greater, indicating an underexplored avenue for growth in Poland’s e-commerce sector. This gap in data underscores the need for a more comprehensive assessment of Poland’s e-export potential, suggesting that the actual figure could be higher and pointing to untapped opportunities for Polish businesses in the international digital marketplace.
I couldn’t find specific data for e-export, but here is a breakdown of main destination of Polish export in general:

source: paih.gov.pl
Implications for e-commerce and SEO in Poland
- Increased consumer spending: As disposable incomes rise, so does the propensity to shop online. E-commerce platforms can capitalize on this by targeting SEO strategies towards high-demand products and services, ensuring visibility in a growing market.
- Cross-border e-commerce opportunities: Poland’s significant role in European production chains and its record-high foreign trade turnover highlight its integration with the global economy. SEO strategies can be tailored to attract not just local but also international customers, leveraging Poland’s strong export sector.
- Tailored SEO for a diversified market: The economic stability and growth encourage a diverse range of businesses to flourish. SEO campaigns must be versatile, catering to a broad spectrum of industries from tech to fashion, and everything in between, mirroring the economic diversity.
- Sustainability and innovation: With the Polish economy’s forward momentum, businesses are increasingly integrating sustainability and innovation into their models. E-commerce and SEO strategies should reflect this trend, targeting the growing demographic of environmentally and socially conscious consumers.
- Attracting foreign investment with SEO: For foreign businesses looking to enter the Polish market, a strong SEO presence can be a key differentiator. Given Poland’s economic stability and growth prospects, positioning oneself prominently in search results can attract not only consumers but also potential investors and partners.
Poland’s economic narrative is one of resilience, growth, and integration with the global market. For e-commerce, this environment is not just a backdrop but a dynamic stage that influences consumer behavior, investment trends, and online marketing strategies. As Poland continues to develop, understanding and leveraging its economic strengths will be crucial for e-commerce businesses and their SEO campaigns, aiming to capture the attention of a confident, spending-ready population. The Polish economy’s health is more than just numbers; it’s a beacon guiding the strategic direction of digital commerce and marketing within and beyond its borders.
Language and cultural factors
In the Polish SEO landscape, while Polish remains the primary language for content and communication, recognizing the sizable Ukrainian community—over 1 million residents—is beneficial for certain businesses. Although incorporating Ukrainian language content isn’t a requirement, it’s a strategic consideration for reaching this significant demographic.
For businesses targeting this group, offering content in Ukrainian can be a valuable addition, enhancing user experience and engagement. Tailoring SEO strategies to include cultural nuances and language preferences of both Polish and Ukrainian audiences can broaden market reach and potentially increase visibility among these diverse groups.
Polish demographics in the context of e-commerce and SEO
Poland’s demographic profile, characterized by its diverse age distribution, significantly influences e-commerce trends and SEO strategies. As of the latest data available up to early 2023, Poland’s population exhibits a broad age range, with a notable proportion of the population in the working-age bracket (20-64 years), alongside substantial younger (<20 years) and older segments (65+ years).
Demographics of Poland impact on e-commerce:
- Younger consumers: The younger demographic, being digital natives, are highly adept at using online platforms for shopping, social media, and entertainment. Their preferences drive demand for trendy, tech-savvy products and services, and they tend to value user experience, social proof, and sustainability. E-commerce targeting this group thrives on fast, mobile-optimized platforms that integrate seamlessly with social media.
- Working-age consumers: This segment, possessing greater purchasing power, focuses on convenience, quality, and value for money. They are likely to engage in online shopping for a wide range of products and services, from electronics and fashion to groceries and financial services. E-commerce strategies targeting this demographic emphasize user-friendly interfaces, comprehensive product information, and robust customer service.
- Older consumers: Although traditionally less engaged with e-commerce, the older population segment is increasingly becoming active online, particularly influenced by the convenience of online shopping. E-commerce platforms can tap into this market by ensuring accessibility, offering clear and detailed product descriptions, and providing excellent customer support.
Polish demographics impact on SEO:
- Content customization: Understanding the diverse age demographics allows for the customization of content to meet the specific interests and needs of each age group. For younger audiences, more dynamic, visually engaging content may be effective, while detailed, informative content may resonate more with older users.
- Keyword strategy: Age-specific interests and search behaviors influence keyword strategy. For instance, younger users might search for the latest tech gadgets or fashion trends, whereas working-age users might look for home improvement products or professional services.
- Mobile optimization: With the younger demographic’s propensity for mobile device usage, ensuring websites are mobile-friendly is crucial for SEO. This includes fast loading times, responsive design, and easy navigation.
- Accessibility: Making websites accessible to older users, through readable fonts, easy navigation, and voice search optimization, can improve SEO outcomes by broadening the user base.
E-commerce dynamics in Poland: An in-depth Look
The digital landscape in Poland has undergone a transformative journey, characterized by robust growth across various facets of e-commerce. Here’s a detailed snapshot capturing the essence of Poland’s e-commerce evolution and consumer behaviors:
- Surge in internet access: From 2012 to 2021, households with internet access soared from 60% to an impressive 96.2%, according to the Central Statistical Office (CSO). This exponential growth has laid a solid foundation for the digital economy.
- Rise in online shoppers: The proportion of Polish internet users engaging in online shopping skyrocketed from 45% in 2013 to 90%. This uptick includes groups traditionally less inclined towards e-commerce, like the older generation and rural dwellers, showcasing a broadening base of digital consumers.
- Market value expansion: The B2C e-commerce market has witnessed a fivefold increase in value, paralleled by a 3.5-fold rise in the B2B e-commerce sector’s value. Furthermore, digital sales’ share in total retail sales has tripled, underlining the growing significance of online commerce.
- Growth in online retailers: The landscape has become more competitive with a 2.5-fold increase in the number of registered online stores, signaling a vibrant and expanding market.
- Consumer preferences and behaviors:
- Mobile shopping: The preference for using mobile devices for online shopping is on the rise, reflecting the global trend towards mobile commerce.
- Social media’s role: Social media significantly influences purchasing decisions, serving as a platform for product discovery, reviews, and ads.
- Marketplace dominance: Platforms like Allegro, AliExpress, Amazon, eBay, and mobile shopping apps such as Temu, Biedronka, Shein, Lidl, Żappka, Vinted, or Rossman are immensely popular among Polish consumers. There are also some new marketplaces emerging nowadays like Rozetka (mainly for Ukrainian immigrants) or Wszystko.pl (developed by one the biggest IT companies – Comarch) or Empik.com (which evolves from a book & media store like Amazone once did).
- Price sensitivity: Shoppers exhibit high price sensitivity, diligently comparing deals across platforms to find the best offers.
- Demand for quick delivery: Fast and reliable delivery services are highly valued, with consumers favoring online stores that can meet these expectations.
- Preferred payment methods: Security and convenience drive the choice of payment methods, with a preference for bank transfers, payment cards, and mobile payment solutions.
- E-commerce event engagement: Polish shoppers actively participate in events like Black Friday and Cyber Monday, which significantly boost online sales.
- Data privacy concerns: There’s an increasing consciousness about personal data security, influencing platform choice.
- Sustainable and local products: A growing segment of consumers is drawn towards sustainable, eco-friendly products and supports local businesses, aligning with global trends towards sustainability and localism.
This comprehensive overview not only highlights the rapid growth and diversification of Poland’s e-commerce sector but also sheds light on the nuanced consumer behaviors shaping the digital market. These insights are crucial for businesses and marketers aiming to navigate the Polish e-commerce landscape effectively, tailoring their strategies to meet the evolving demands and preferences of Polish consumers.
Polish e-commerce in 2023 – brief summary
Now take a look at main events in Polish e-commerce in 2023 (according to Manager Plus):
- New entrants: Three new e-commerce platforms launched in Poland: Rozetka (a leader from Ukraine), Wszystko.pl (by Comarch), and Temu (from China).
- Market value: The Polish e-commerce market was projected to reach a value of approximately 124 billion PLN by the end of 2023.
- Rozetka’s strategy: Starting operations in June, Rozetka aimed to replicate its Ukrainian success in Poland, leveraging its existing warehouse in Poland for more efficient deliveries.
- Wszystko.pl’s launch: Comarch’s Wszystko.pl began operations on June 29, offering a platform with 15,000 sellers registered at launch, growing to nearly 20,000 by mid-November.
- Temu’s social media dominance: Despite being a new entrant, Temu quickly gained over 13 million users by November, outpacing all but Allegro in Poland, thanks to aggressive social media and Google Ads campaigns.
- Shopee’s marketing and exit: Shopee’s aggressive marketing campaign reached over 30% of Poles within eight months. However, high marketing costs and low sales led to its exit from the Polish market in January 2023.
- Consumer response: Rozetka reported a 57% increase in orders and a 16% increase in average basket value in November compared to October, indicating positive consumer reception.
- Controversies: Temu faced controversies regarding data security and privacy, with experts cautioning about the app’s access to unnecessary data.
Regulations and controlled niches
In Poland, as in the rest of Europe, running a business and managing e-commerce operations are subject to a complex regulatory environment that significantly influences how companies operate. Key among these regulations are stringent privacy laws under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which mandates rigorous data protection and privacy practices, impacting how businesses collect, store, and process personal data. Consumer rights are also strongly protected, with regulations ensuring transparency, the right to return products within 14 days, and safeguards against unfair commercial practices. Competition laws further ensure fair play in the market, preventing monopolies and fostering a healthy market environment. Given these intricacies, foreign businesses often find it beneficial to partner with local companies well-versed in navigating the Polish and European legal landscapes, thereby minimizing the risk of non-compliance.
Specifically, industries such as medical products, finance, gambling, drugs, alcohol, and THC and CBD products face additional layers of regulation. For instance, medical products and pharmaceuticals require approval from relevant health authorities, adhering to strict safety and efficacy standards. Financial services are regulated to protect consumers and ensure the stability of the financial system, requiring specific licenses. The sale of drugs and alcohol is tightly controlled, with age restrictions and licensing requirements. Similarly, THC and CBD products, despite growing in popularity, are subject to legal thresholds for psychoactive compounds and require careful navigation of both Polish and EU regulations.
In conclusion, successfully running an e-commerce business in Poland demands a thorough understanding of the local and European regulatory framework. Privacy laws, consumer protection, competition policies, and sector-specific regulations shape the business landscape, making cooperation with local experts not just beneficial but often necessary to ensure compliance and avoid costly mistakes.
Competition on Polish market: challenges and opportunities
The Polish e-commerce landscape presents a complex mix of challenges and opportunities for new entrants and existing players. In nearly every developed sector, from banking and finance to health & beauty, automotive, and electronics, dominant players and well-established brands have cemented their positions, making the market highly competitive.
The competition is fierce, with industry giants, corporations, and established brands having extensively targeted both short, mid, and long-tail keywords. This comprehensive approach to SEO has made it increasingly difficult for new entrants to gain visibility and traffic solely through high-quality content targeting long-tail phrases.
Certain sectors such as banking, finances, health & beauty, automotive, and electronics are especially competitive. In these areas, main players not only have developed comprehensive long-term strategies but have also built solid link profiles, further solidifying their market dominance.
Despite the dense market, there are still numerous opportunities for businesses to build their presence in Google’s search channel. The landscape is not static, and the latest algorithm updates have introduced changes that challenge the hegemony of the biggest online shops and marketplaces.
These changes provide a window of opportunity for new and smaller players. With a perfectly tailored SEO strategy and an adequate budget, making a mark in the Polish e-commerce market is still within reach. The key lies in identifying niches or consumer needs that are underserved by the major players, leveraging local SEO, optimizing for mobile, focusing on user experience, and engaging in creative content marketing strategies.
Success in this competitive environment requires agility and the ability to adapt to the latest SEO trends and algorithm changes. Businesses must continuously analyze their SEO strategies and be ready to pivot based on market feedback and the evolving digital landscape.
Building a solid link profile and developing long-term content and SEO strategies are essential. While the competition with industry giants can be challenging, focusing on unique value propositions, exceptional customer service, and a strong online presence can help smaller players carve out their niche.
Despite the competitive landscape, entering the Polish e-commerce market is likely still more cost-effective and easier compared to more mature markets like Germany, France or Great Britain. The relative affordability of advertising, SEO services, and the cost of establishing an online presence in Poland offers a strategic advantage for businesses looking to expand their footprint in Europe. This economic factor, coupled with Poland’s growing digital consumer base, makes it an attractive entry point or expansion target for companies aiming to establish or enhance their presence in European markets.
While the challenges are significant, the evolving nature of search algorithms and consumer preferences means that opportunities are always present for those ready to innovate and adapt. Success hinges on understanding the nuances of the Polish e-commerce market, leveraging the latest SEO techniques, and committing to a long-term vision that prioritizes user experience and value.
Legal aspects of e-commerce in Poland
For businesses operating in the Polish e-commerce market, aligning with GDPR requirements and the recent implementation of the Omnibus Directive is critical. These regulations not only ensure consumer protection but also establish a legal framework that e-commerce platforms must navigate carefully. Here’s a detailed overview, incorporating the importance of database security, privacy settings, information obligations, and anti-spam regulations.
GDPR compliance
- Visible cookie consent banners: Websites must display clear cookie consent banners that allow users to accept or reject cookies, with a detailed explanation of cookie use.
- Privacy policies: Privacy policies must be comprehensive, easily accessible, and in plain language, detailing how consumer data is collected, used, stored, and protected, adhering to EU regulations.
Omnibus Directive impact on e-commerce in Poland
The Omnibus Directive introduces significant changes across several laws, impacting the e-commerce industry notably. These include the Law on Consumer Rights, the Law on Counteracting Unfair Market Practices, and the Law on Information on Prices of Goods and Services.
Information obligations
E-commerce businesses are now required to provide detailed information at the point of contract agreement, including means of online communication, disclosures on price adjustments based on automated decision-making, and the elimination of outdated requirements like trader’s fax number disclosure.
New regulations for trading platforms
Definitions and obligations for online trading platforms have been clarified, including transparency on listing placements, disclosure of trader status, applicability of consumer protection laws, and shared obligations between sellers and platform providers.
Strict control of customer reviews
Businesses must inform consumers if and how they verify that reviews are from actual users. Misleading practices include posting false reviews or failing to take steps to verify the authenticity of consumer opinions.
Transparency in price information
Traders must now list the lowest price of a product 30 days prior to a price reduction alongside the new price, enhancing transparency. This requirement extends to both goods and services in Poland, exceeding EU mandates for goods alone.
Additional compliance considerations
- Database security: Implementing robust security measures to protect consumer data databases from breaches is essential under GDPR.
- Privacy settings: Offering users control over their privacy settings, enabling them to manage how their data is used and shared.
- Information obligations: Businesses must regularly update consumers about how their data is being used, ensuring transparency and trust.
- Anti-spam regulations: Adhering to strict regulations about sending commercial emails, requiring explicit consent from recipients before sending marketing messages.
For businesses in the Polish e-commerce sector, understanding and implementing these regulations is not just about legal compliance; it’s also a cornerstone of building consumer trust and creating a transparent, user-friendly shopping environment. By prioritizing these elements, businesses can not only avoid potential fines and legal challenges but also enhance their reputation and customer satisfaction in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
Chapter 2: practical aspects of SEO in Poland
Technical SEO fundamentals
To navigate the complexities of Poland’s online environment effectively, employing both technical and strategic SEO tactics is crucial. Here’s a deeper dive into how to refine your website for peak performance in visibility, accessibility, and search engine rankings:
Website Localization Tactics
Registering a .pl domain is a strategic move that can significantly boost your site’s relevance and visibility in local search results. It acts as a clear indicator of your business’s dedication to serving the Polish market, potentially improving trust and engagement with local customers. You may also consider using .pl/ua/ address structure to add seperate catalogue for Ukrainians in Poland.
Regarding on chosen TLD strategy, implementing the “hreflang” tag specifically with “pl-PL” can be vital for signaling to Google that your content is intended for a Polish-speaking audience. This ensures that your pages are accurately presented to users searching in Polish, optimizing user experience and engagement. You may also
Mobile optimization
With the widespread use of smartphones in Poland, it’s imperative that your website is fully responsive. This means it should automatically adjust to provide an optimal viewing experience across a variety of devices, from desktops to smartphones.
Tools like Google’s Lighthouse are instrumental in analyzing and enhancing your site’s performance, particularly for mobile users. Improving loading times is crucial, as mobile users often rely on quick access to information on the go. Faster site speeds lead to better user satisfaction and can contribute to higher rankings in search results. Also remember about Google’s Core Web Vitals requirements.
Hosting / Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Utilizing a CDN with servers located in Poland or neighboring countries can decrease your site’s load times for local users. By storing copies of your site on multiple servers around the region, a CDN ensures that users access your site from the closest possible location, minimizing delays and improving the user experience.
Poland offers a diverse range of hosting providers, from well-established giants to smaller, specialized companies, each with its unique strengths. You can choose among brands like OVH, Home.pl or CyberFolks, but also pick one from a big variety of smaller players like theCamels, Kei, Kru.pl, SmartHost, Hostersi, dHosting, zenbox, LH.pl, AZ, SEOhosting.pl just to name few.
Structured data
Applying schema.org structured data helps search engines better understand the content and context of your site. For instance, using the LocalBusiness schema can enhance the visibility of shop details in search results, while the Product schema allows you to highlight e-commerce items complete with prices in PLN. These schemas enable richer, more informative search results, which can improve click-through rates.
Given the price sensitivity of Polish customers, it’s essential to highlight aspects of your e-commerce offering that can sway purchasing decisions. Utilizing schema markup effectively can help emphasize these key selling points directly within search results, making your products more appealing to potential buyers. Consider incorporating the following strategies into your website’s schema markup to cater to the Polish market’s preferences:
- Use the OfferShippingDetails schema to detail your shipping policies, particularly highlighting free delivery options. This information can appear in search results, immediately showing potential customers that you offer this cost-saving benefit.
- Implement the Product schema to include information about your return policies, such as the number of days customers have to send products back. This transparency not only builds trust but also addresses the concerns of hesitant shoppers, making them more likely to commit to a purchase.
SEO-friendly URLs:
Including Polish characters in your URLs not only improves the accuracy of your keyword targeting but also resonates more authentically with local users. This practice enhances your content’s relevance for searches conducted in Polish, aiding in better search alignment and visibility. Also remember about displaying proper breadcrumbs in SERP’s.
Content strategy for SEO in Poland
Crafting content SEO strategies for the Polish market requires a nuanced approach, taking into account the unique preferences and behaviors of Polish internet users. Here are some tailored strategies based on extensive experience in the Polish SEO landscape:
Emphasize video and multimodal content
Polish audiences favor fast, easily digestible media. Incorporating video content and other multimodal formats caters to this preference, enhancing engagement and retention.
Given the tech-savviness of Polish SEO specialists and their quick adoption of AI in content creation, it’s crucial to produce content that is not only relevant and engaging but also factually accurate.
Build trust through reliable content
With a proliferation of unreliable content online, Polish consumers have grown cautious. It’s essential to establish credibility by aligning with popular brands, bloggers, and influencers who already have the trust of your target audience.
Incorporating social proof, such as user reviews, expert opinions, and endorsements from trusted Polish experts, can significantly boost your brand’s reliability. Western brands often carry more trust than those from eastern regions or emerging markets, highlighting the importance of presenting a strong, trustworthy brand identity.
Content marketing best practices
Following Google’s helpful content system, prioritize creating content that genuinely addresses user needs. Lists, summaries, key takeaways, and data-driven insights can make your content more accessible and valuable to users.
Sponsored content is highly effective in Poland, provided it leans more towards offering advice and value rather than overt advertising. High-quality content marketing and native advertising are preferred, with platforms like Whitepress or Linkhouse being popular for facilitating these connections. However, it’s crucial to maintain a balance and ensure content remains informative and engaging.
Challenges in content collaboration
Establishing guest blogging and outreach collaborations can be challenging due to the commercial expectations of publishers and bloggers. Many are aware of the monetization potential of their platforms, making purely informational collaborations less common.
In conclusion, a successful content SEO strategy for the Polish market must be multifaceted, combining engaging and multimodal content with a strong emphasis on trustworthiness and reliability. By leveraging popular platforms and influencers, providing valuable and factual content, and navigating the commercialized landscape of content collaboration with tact, businesses can effectively engage Polish audiences and build a strong online presence.
SEO tools and technology in Polish SEO
Polish SEO professionals are renowned for their tech-savviness, a trait that significantly shapes the SEO landscape in Poland. This technological adeptness is evident in the way agencies and individual specialists harness the power of advanced tools and platforms to optimize their SEO strategies. For instance, agencies like mine takaoto.pro are at the forefront of innovation, developing proprietary tools that cater to specific SEO needs, demonstrating a deep understanding of the digital environment and the necessity for bespoke solutions. Content planning, creation, data analysis, translations – it becomes more and more automated nowadays.
The use of APIs to create custom tools for indexation and SEO analysis is widespread among Polish SEO experts. This approach allows for a tailored analysis of web data, enabling more precise and effective optimization strategies. The development of such tools underscores the Polish SEO community’s inclination towards leveraging technology to enhance efficiency and outcomes.
Poland has also made a significant mark on the global SaaS market with popular brands like Senuto, SurferSEO, and Contadu, with its AI-powered Neuron Content Writer. These platforms offer sophisticated SEO and content marketing solutions, reflecting the high level of technical expertise within the Polish SEO sector.
Moreover, the ecosystem is supported by marketplaces that facilitate collaboration between advertisers, link builders, content marketing specialists, and bloggers/publishers. This network fosters a vibrant community where resources and opportunities can be easily accessed, enhancing the overall effectiveness of SEO campaigns.
The integration of AI into tool development is another area where Polish SEO professionals excel. By building AI-driven tools, they are able to automate and refine processes such as content creation, keyword research, and data analysis, staying ahead in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
In summary, the tech-savviness of Polish SEO professionals is a defining characteristic that drives innovation and excellence in the field. Through the development of specialized tools, adoption of AI technologies, and participation in collaborative marketplaces, they continue to set high standards for SEO practices both in Poland and internationally.
Link building tactics in Poland
The Polish approach to link building is pragmatic and results-oriented, often summarized by the ethos of “whatever works.” There’s a healthy skepticism towards Google’s official statements, with a preference for empirical evidence over theoretical guidelines. Polish SEO professionals are not afraid to push boundaries and experiment with various tactics to see what truly impacts rankings. In the fiercely competitive Polish market, adopting an aggressive stance is sometimes seen as necessary—embodying a “go hard or go home” mentality. This practical, test-and-learn approach ensures strategies are honed through real-world application, ensuring they stand up to the demands of a competitive digital landscape.
When developing a link-building strategy for the Polish market, several innovative tactics can significantly enhance your SEO efforts. Here’s a refined approach to incorporating these strategies:
Embrace sponsored articles
- Access major media outlets: Utilize sponsored articles to gain visibility on prominent Polish media platforms, ensuring your brand stands out.
- Backlink management: exercise control over your backlinks by opting for both yearly and lifetime placements, depending on your strategy.
- Strategic communication: Tailor your message to align with your brand’s voice, ensuring it doesn’t get lost among multiple outbound links in an article.
- Anchor texts: Maintain control over your anchor texts to optimize relevance and SEO impact.
- Don’t follow just basic metrics like DR, AS etc. Focus on website’s health, visibility trends, link profile in details and links in/out ratio.
Prioritize local backlinks
- .pl Domains: Seek out backlinks from reputable Polish websites with .pl domains to enhance your domain authority within the local market.
Utilize expired domains and PBNs
- Domain history checks: Use tools like the Wayback Machine and Ahrefs to investigate a domain’s history before purchase, avoiding those penalized or associated with spam.
- Cautious PBN use: While PBNs can be effective, they require careful management to avoid search engine penalties.
- Expired domains: Explore Polish platforms such as aftermarket.pl or premium.pl for expired domains that offer SEO benefits, leveraging their existing authority.
- 301 redirects: Don’t overlook the effectiveness of 301 redirects from relevant, high-quality domains.
Leverage NAPs and local link building
- Local SEO: Enhance your local business presence with local links and Google My Business listings, crucial for local SEO success.
Out of the box tactics and competitive analysis
- Study your competitors: Analyzing your competitors’ link-building tactics can reveal niche-specific opportunities. Remember that many links (especially PBN’s) can be hidden from tools like Ahrefs, Majestic or Semrush. Try more niche tools like SEO Spyglass to uncover true link profiles of black hat SEO tactics run by your competitors.
- Beyond traditional links: Consider acquiring links from job boards, public sites, or through media patronage for events.
- Industry events: Position your specialists as speakers at industry events, particularly in sectors like marketing, e-commerce, and IT, to gain valuable backlinks.
- You can also try buying links from other than Polish TLD’s (that’s part of my speech on SEO Mastery Summit).
Incorporating these strategies into your link-building efforts in Poland requires a blend of traditional SEO wisdom and creative, market-specific tactics. By focusing on sponsored content, local backlinks, the strategic use of expired domains and PBNs, and leveraging unique opportunities for visibility, you can build a robust link profile that supports your SEO objectives and enhances your online presence in the Polish market.
SEO services in Poland
In Poland, SEO services typically operate on indefinite contracts, with a focus on monthly sprints and corresponding monthly payments. This structure allows for flexibility and ongoing optimization, ensuring that strategies can evolve in response to market changes and performance data. Agencies like ours provide a comprehensive suite of services, including consulting, analysis, planning, and execution, covering everything from content marketing and link building to technical audits. The pricing for these services varies widely, influenced by factors such as the industry involved (impacting competition level) and the project’s scale.
Our expertise isn’t limited to the Polish market; we also specialize in campaigns across other Central and Eastern European (CEE) markets. We’re adept at working alongside in-house marketing teams, IT and copywriters, aligning our efforts with your brand’s overall strategy. The deeper our understanding of your business, the more customized and effective our SEO solutions become. A commitment to understanding your goals and available resources is key to maximizing the benefits of our collaboration.
Language barriers are virtually non-existent, as most Polish SEO professionals are proficient in English, particularly for written communications like emails and project management tools such as Trello and Asana. Many of us are also fluent in spoken English, facilitating regular video calls without any issues.
Let me know about your needs
To initiate our collaboration, we invite you to share details about your objectives, existing strategies, and the resources you’re willing to dedicate to your SEO project, including budget, personnel, time, content, and technology. Armed with this information, we can craft a bespoke proposal tailored to your specific needs.
Our goal is always to reach the top positions on Google for you, but initially, we’ll need to determine what can be realistically achieved with your budget. If your ambitions include outperforming competitors, we’re ready to provide estimates on the time and investment required to achieve those goals.
—
Most important data sources:
- Why Poland, Polish Investment & Trade Agency, paih.gov.pl/en/why_poland/economic_stability_and_a_strong_economy/
- 5 facts about Polish export – PwC, pwc.pl/pl/publikacje/2019/5-faktow-o-polskim-e-eksporcie-raport-pwc.html
- E-commerce in Poland, Ministry of Economic Development and Technology, trade.gov.pl/en/news/e-commerce-in-poland/
- E-commerce 2023 debuts and disappointments, Manager Plus, managerplus.pl/e-commerce-w-polsce-w-2023-roku-debiuty-i-rozczarowania-93883
- Gross domestic product & GDP in Poland, Statista, statista.com/statistics/263588/gross-domestic-product-gdp-in-poland/
- Decade of Polish e-commerce, 2013 – 2023 | e-Chamber Report, ecommerce-europe.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/The-e-Chamber-Report-a-Decade-of-Polish-E-commerce.pdf
- 10 facts about Polish e-consumers 2023, Gemius,
- Central Statistical Office of Poland (Główny Urząd Statystyczny – GUS), stat.gov.pl
- Eurostat, ec.europa.eu/eurostat